LAW
Why You Should Consider a Whistleblower Lawyer When Reporting IRS Fraud

Understanding the IRS Whistleblower Program
The IRS Whistleblower Program is designed to encourage citizens to report tax evasion, fraud, or other tax-related misconduct by offering substantial monetary rewards. Whistleblowers are eligible to receive between 15% and 30% of the amount the IRS collects based on their information, provided it leads to successful actions against tax law violators. The process is confidential, encouraging individuals to come forward without fear of public exposure or retaliation. Over the past decade, this initiative has played a critical role in uncovering major tax frauds and recouping billions for U.S. taxpayers. Dedicated channels and resources make it easier for individuals to report issues. Still, the complexities of tax law often require expert support from a whistleblower attorney who can navigate both the filing and follow-up phases.
Navigating IRS whistleblower rules, deadlines, and evidence requirements is complex, and mistakes can jeopardize both protection and potential compensation. Securing a knowledgeable legal advocate early helps ensure you understand your rights and responsibilities, avoid pitfalls like employer retaliation or procedural issues, and increase your chances of success. Professional guidance is essential given evolving laws, high financial stakes, and the potential for complicated legal proceedings. Similar protections and incentives also exist through other federal programs.
The Role of a Whistleblower Lawyer
A whistleblower lawyer provides far more than just basic legal consultation. From the earliest stages of filing, these attorneys strategize how best to present evidence and maximize the impact of your information. They can help you understand which aspects of your case qualify for maximum rewards, clarify procedural steps, and prepare you for interactions with government investigators.
Another vital service whistleblower lawyers provide is managing confidentiality. Ensuring your name and details of your complaint remain protected reduces the risk of workplace retaliation or social backlash. The IRS offers certain protections, but a skilled attorney is instrumental in enforcing these measures and advocating for your rights if they are ever challenged.
Benefits of Legal Representation
- Expertise in Tax Law: Whistleblower lawyers possess specialized knowledge that enables them to interpret intricate sections of the U.S. tax code, anticipate procedural issues, and present your evidence in the most effective manner possible. Their expertise is significant for maximizing your eligibility and ensuring you meet all legal requirements.
- Protection Against Retaliation: Confronting a current or former employer can feel daunting. Attorneys can guide you on the safeguards provided by federal whistleblower laws and take legal steps if your rights are infringed. For more information, explore federal whistleblower protections through the IRS.
- Maximizing Potential Rewards: The reward structure is dependent on how essential and new your information is. Attorneys know how to present your case to optimize potential compensation and avoid common missteps that could lead to dismissal or a reduction in payouts.
Case Studies Highlighting the Importance of Legal Counsel
Legal complexities are well-documented in whistleblower cases. For example, a recent U.S. appeals court case found that a corporate attorney who alerted the SEC to suspected fraud was denied a whistleblower award because they failed to meet technical filing criteria. Cases like these reinforce the necessity of experienced legal representation to navigate ever-changing rules and requirements. Such legal battles highlight both the risks and the high standards expected by government agencies. Read more about the appellate ruling at Reuters’ report. Working with a knowledgeable whistleblower lawyer can prevent costly mistakes and improve the chances of a successful claim. Their guidance ensures that procedural and evidentiary requirements are met from the outset, reducing the likelihood of disqualification.
Steps to Take When Considering Reporting IRS Fraud
- Gather Evidence: Collect comprehensive documentation supporting your claim, including emails, contracts, financial records, and other direct evidence of the suspected fraud.
- Consult a Whistleblower Lawyer: Schedule a confidential consultation with a specialized attorney to assess your case’s merits and receive guidance on safely moving forward.
- File Form 211: With the assistance of your lawyer, accurately complete and submit IRS Form 211, which is the official tool to begin a whistleblower claim.
- Maintain Confidentiality: Avoid public disclosure and discussing your case with anyone outside your legal counsel to protect your identity and prevent undermining the investigation.
Potential Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Whistleblowers frequently confront hurdles such as workplace retaliation, difficulty obtaining evidence, and navigating bureaucratic processes. There are legal protections in place, but enforcing these rights often demands expertise and vigilance. Lawyers mitigate these risks by advocating zealously for your interests, preserving your legal claims in the event of workplace discipline or termination, and managing complex relations with government investigators. Where evidence is hard to obtain, attorneys can advise on legal means of access.
Conclusion
Stepping forward to report IRS fraud is a courageous act that serves the public interest. The IRS Whistleblower Program can provide substantial financial rewards and safeguards, but success is far more likely with the support of an experienced attorney. By working with a whistleblower lawyer, you protect your rights, maximize your possible reward, and ensure your efforts contribute to the integrity of the tax system.
LAW
Understanding the Complexities of Trust Administration: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction to Trust Administration
Trust administration is a critical process in the management of assets placed into a trust, designed to ensure that the wishes of the grantor are fulfilled and that beneficiaries receive their entitlements in accordance with legal and fiduciary requirements. At its core, trust administration involves the oversight, organization, and management of assets and obligations specified by a trust document, often guided by a trustee who has been entrusted with these responsibilities. The significance of effective trust administration cannot be overstated, as improper management or neglect can lead to legal disputes, financial losses, and even the unintended misallocation of trust assets. Trustees must operate with a combination of financial acumen, legal awareness, and ethical integrity to ensure that the trust functions smoothly over its duration.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Trustee
The trustee is the central figure in trust administration and bears the fiduciary responsibility of acting in the best interests of the beneficiaries while adhering strictly to the terms of the trust. The responsibilities of a trustee are multifaceted, including asset management, investment oversight, tax reporting, and distribution of income or principal to beneficiaries as dictated by the trust agreement. Trustees must balance prudence with opportunity, making strategic decisions that preserve and grow trust assets while mitigating risk. Furthermore, trustees are expected to maintain meticulous records of all financial transactions, communications with beneficiaries, and decisions made in the course of trust management. This transparency ensures accountability and can protect the trustee from potential liability or claims of mismanagement.
Key Elements in Trust Administration
Effective trust administration requires attention to several key elements. First, there is the proper identification and management of trust assets. Assets may range from cash and securities to real estate and personal property, each requiring unique handling and valuation. Trustees must ensure that assets are appropriately safeguarded and that any necessary insurance, maintenance, or oversight is provided. Second, tax compliance is an essential component of trust administration, requiring the trustee to understand complex tax codes, prepare returns for the trust, and sometimes coordinate with financial advisors or tax professionals to optimize tax efficiency. Third, the distribution of assets according to the terms of the trust demands precision, fairness, and an understanding of both the trust’s intent and the beneficiaries’ legal entitlements. Failure in any of these areas can have severe financial and legal repercussions for both the trustee and the beneficiaries.
Legal Considerations in Trust Administration
Trust administration is heavily regulated by state and federal laws, which define the rights of beneficiaries and the responsibilities of trustees. Trustees must comply with statutes governing fiduciary duties, investment practices, reporting requirements, and dispute resolution procedures. In addition, they must understand the nuances of the trust instrument itself, as trust language can sometimes be ambiguous or open to interpretation. Legal challenges can arise when beneficiaries question the trustee’s decisions, such as investment strategies, timing of distributions, or administrative expenses. Therefore, proactive communication, careful documentation, and adherence to both legal standards and the trust’s terms are critical to preventing conflicts. Trustees often work closely with attorneys specializing in estate planning or trust law to ensure that every action taken aligns with both the legal framework and the intent of the trust creator.
Financial Management in Trust Administration
The financial component of trust administration is perhaps the most complex and demanding aspect of the role. Trustees must not only preserve trust assets but also make prudent investment decisions that balance risk and return. This requires a deep understanding of financial markets, portfolio management, and the specific financial goals outlined in the trust document. Many trusts include provisions requiring conservative investments, while others allow for more aggressive strategies to grow wealth for beneficiaries. Trustees are also responsible for managing cash flow, paying trust expenses, and forecasting the financial needs of beneficiaries over time. Investment decisions must be made with careful documentation and justification, as beneficiaries have the right to question the trustee’s approach if they believe it fails to meet fiduciary standards. Effective financial management in trust administration combines analytical skill, patience, and an ethical commitment to acting in the best interests of the beneficiaries.
Communication and Beneficiary Relations
A crucial yet often overlooked component of trust administration is the ongoing communication with beneficiaries. Trustees are expected to provide clear and timely information about trust performance, distributions, and any significant decisions or changes in strategy. Open communication helps build trust and can prevent misunderstandings that might lead to disputes. Trustees must also be sensitive to the differing needs and expectations of beneficiaries, which may include children, spouses, or charitable organizations. Maintaining transparency and responsiveness in all interactions is fundamental to fulfilling fiduciary obligations and fostering positive relationships. In addition, trustees must navigate challenging situations diplomatically, especially when beneficiaries disagree about distributions or interpret trust provisions differently. Properly managed communication enhances the overall effectiveness of trust administration and ensures the long-term success of the trust’s objectives.
Challenges and Common Issues in Trust Administration
Despite careful planning, trustees often face challenges in the administration of trusts. These may include complex family dynamics, disagreements among beneficiaries, volatile market conditions, or unclear trust provisions. Trustees may also encounter administrative difficulties, such as accurately valuing unique assets, handling tax complexities, or managing multiple beneficiaries with competing needs. Additionally, trustees must guard against conflicts of interest, as any perception of self-dealing or bias can result in legal liability. Successfully navigating these challenges requires a combination of legal knowledge, financial expertise, and emotional intelligence. Proactive problem-solving, meticulous record-keeping, and consistent adherence to fiduciary duties are essential to overcoming obstacles and maintaining the trust’s integrity.
Technological Advancements and Trust Administration
In recent years, technology has begun to play a significant role in trust administration, offering tools that simplify record-keeping, reporting, and communication with beneficiaries. Digital platforms allow trustees to track assets, generate financial statements, and provide beneficiaries with secure access to relevant information. Moreover, technology can facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements and reduce administrative errors. However, trustees must also be vigilant about cybersecurity risks, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected from unauthorized access or breaches. Integrating technology thoughtfully into trust administration can improve efficiency, accuracy, and transparency, allowing trustees to focus more effectively on strategic decision-making and fiduciary responsibilities.
Conclusion
Trust administration is a complex, multifaceted process that requires a careful balance of legal knowledge, financial acumen, and ethical responsibility. Trustees play a pivotal role in safeguarding assets, ensuring compliance with laws, and fulfilling the intentions of the trust creator for the benefit of the beneficiaries. By understanding the responsibilities involved, staying informed about relevant regulations, and maintaining clear communication with beneficiaries, trustees can navigate the complexities of trust administration successfully. In an era of evolving financial and technological landscapes, effective trust administration continues to demand diligence, foresight, and an unwavering commitment to fiduciary principles, ensuring that the objectives of the trust are met and that the interests of beneficiaries are protected for generations to come.
LAW
How to Stay Informed and Prepared After a Car Accident

Car accidents happen when you least expect them, often leaving you feeling overwhelmed or unsure of your next steps. But being prepared and well-informed can smooth your path to physical, emotional, and financial recovery. In the moments and months following an accident, knowing what actions to take—whether it’s prioritizing your well-being, understanding your legal landscape, or staying connected with support resources—can make all the difference. If you’re navigating this challenging time in Central Florida, you may consider guidance like a Ward Law car accident attorney in Orlando, FL, to help you understand your rights and next steps.
Panic and confusion are common in the aftermath, but having an effective plan empowers you to act swiftly, gather crucial evidence, and advocate for your best interests. The following guide breaks down every essential step, from what to do at the scene to managing claims and personal recovery. With a clear understanding—and the right advocates on your side—you can face this adversity stronger and more resilient.
Immediate Steps to Take After an Accident
Your first priority should always be safety: move to a safe location if possible, check on all parties involved, and call emergency services if injuries or significant vehicle damage have occurred. As you wait for responders, begin documenting the scene. Snap clear photos from multiple angles, noting the vehicle’s position, street signs, road conditions, and any visible injuries. Speak with witnesses to collect their statements and contact details, as this testimony can prove vital in insurance and legal proceedings. Medical evaluation is essential—even if you think you’re unhurt—since some injuries, like whiplash or concussions, may only be detected through professional assessment.
At this stage, maintaining a composed demeanor helps you avoid disclosing unnecessary details to the other driver or insurance representatives. Avoid signifying fault or making any official statements until you’re fully aware of your rights and have consulted legal counsel if needed.
Understanding Your Insurance Policy
Prioritize understanding your insurance policy before an accident ever occurs. Familiarize yourself with vital terms like “liability coverage,” “personal injury protection,” “comprehensive,” and “deductible.” Policies can be complex, hiding important details in fine print, so don’t hesitate to reach out to your insurance agent with questions or clarifications. This preparation ensures that you don’t encounter unanticipated denials or delays during the claims process. Remember, many policyholders overlook essential clauses about rental vehicles, uninsured motorists, or medical coverage, which could dramatically affect your out-of-pocket expenses.
Keep your policy documents in both digital and physical formats for easy access when needed. It’s also prudent to periodically check for updates or amendments in your coverage terms—insurance companies often revise policy language or benefits annually.
Maintaining Organized Records
From the outset, establish a system for tracking all aspects related to your accident. Start a detailed journal of your medical visits, treatments, prescription medication, and physical or emotional symptoms. Save receipts for all accident-related expenses, such as tow truck fees, car rentals, or assistive devices. Record your conversations with insurance agents, adjusters, or legal experts in a dedicated notebook or app, including dates, names, and summaries of the discussions. Meticulous documentation ensures you have the details to contest inaccuracies, substantiate your claims, and present a well-organized file should legal conflict arise.
Digital tools and cloud storage can facilitate secure recordkeeping, allowing you to back up vital documents and access them from anywhere—especially helpful if recovery keeps you away from home for extended periods.
Staying Informed About Your Recovery
Your recovery may be lengthy, involving not only physical healing but also navigating complex insurance and legal frameworks. Keep in touch with your healthcare providers to monitor your recovery and attend all follow-up appointments, both for documentation and to ensure your well-being. Be proactive in understanding the status of your insurance claim and any upcoming deadlines. Should you face litigation or settlement, stay engaged with your attorney and ask questions about timelines, possible outcomes, and required actions on your part. This involvement keeps you prepared and reduces anxiety about the unknown.
Leveraging Technology for Documentation
Today’s technology provides powerful tools to help you stay organized throughout your recovery and claim process. Use calendar apps for reminders about medical visits or legal deadlines, health app trackers for medication routines, and cloud storage solutions for digital copies of all critical documents. Many mobile apps are specifically tailored for accident victims, making it easy to quickly capture photo evidence, input accident details, and generate PDF reports for your records. These digital aids can streamline communication and provide instant access during stressful conversations with insurers or legal teams.
Seeking Professional Guidance
The complexities of accident recovery often demand professional assistance. Consulting a personal injury attorney ensures your rights are upheld and that you pursue all available compensation. Financial advisors can also help if your injury results in a loss of income or unexpected medical expenses. In many cases, the consultation fee is minimal or contingent upon a successful outcome. Applying professional guidance early can save you time, reduce stress, and improve your overall recovery prospects.
Engaging with Support Networks
The emotional aftermath of a car accident can be just as overwhelming as the physical recovery. Lean on your existing relationships and consider joining support groups—both in-person and online—where survivors can share their journeys and coping strategies. These networks provide not only validation and empathy but also practical advice and recommendations for local services. Trusted communities can connect you with specialists, advocacy programs, or recommend additional resources tailored to your specific recovery needs. Support is vital for emotional balance and holistic healing during challenging times.
Conclusion
Navigating the period after a car accident is never easy, but informed preparation and clear action steps can help transform a chaotic circumstance into a manageable and proactive process. By prioritizing safety, thoroughly documenting your actions, understanding your insurance, and staying engaged with professional and personal support resources, you can protect your well-being and future interests. Whether you’re on the road to medical recovery or managing complex claims, taking these steps sets a foundation for resilient, informed self-advocacy in the wake of a traumatic event.
LAW
Common Auto Defects Covered by Lemon Laws
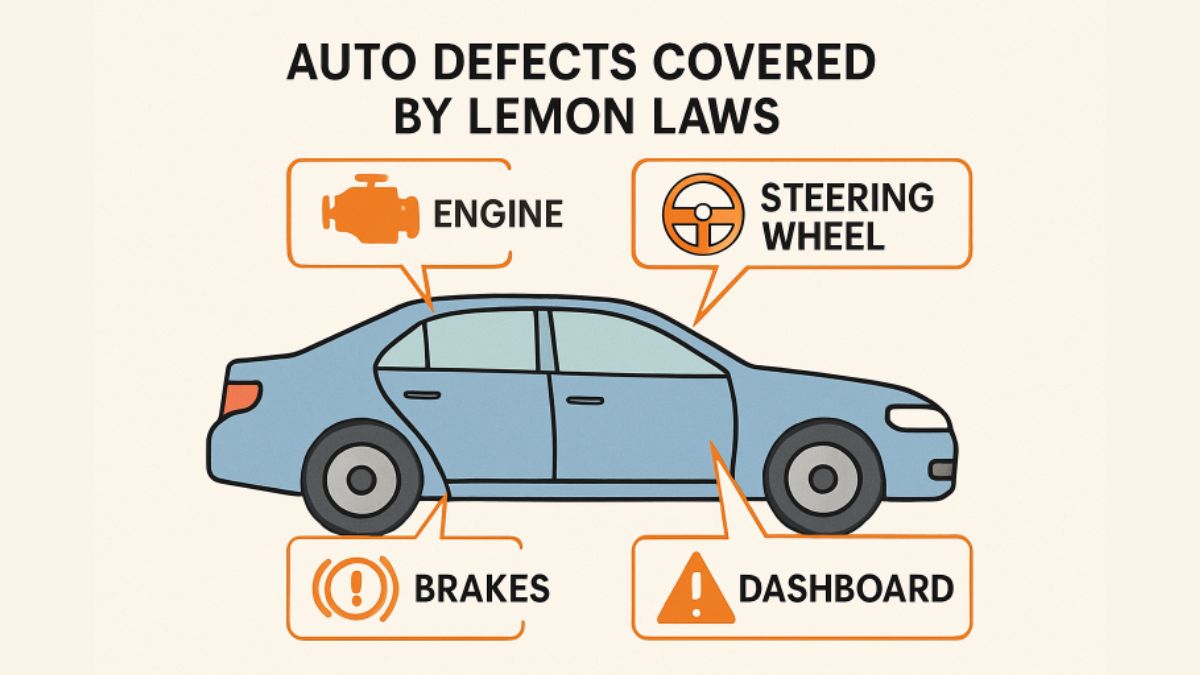
Buying a new vehicle is a significant investment, and when issues arise that threaten the car’s reliability, performance, or safety, it can be frustrating and even dangerous. While manufacturers generally strive to produce defect-free vehicles, some owners experience persistent problems that aren’t resolved after reasonable repair attempts. Lemon laws exist to protect consumers who find themselves in this situation, offering remedies such as refunds, replacements, or cash settlements. For car buyers in states like Maine, consulting a Maine lemon law attorney can be a valuable step to ensure their rights are fully protected and to get a better understanding of potential remedies. Recognizing which defects qualify under lemon laws is a crucial first step to navigating these consumer protections effectively.
Auto defects covered by lemon laws are those that significantly impair the vehicle’s use, value, or safety. Common covered issues, such as electrical malfunctions and brake problems, aren’t just inconvenient—they can diminish safety for drivers, passengers, and everyone on the road. Knowing the signs of a “lemon,” along with the process and qualifications for filing a claim, empowers car owners to take action without delay.
Engine and Transmission Issues
Engine and transmission defects are among the most severe issues that can occur in a vehicle. Symptoms might include the engine stalling while driving, unexplained overheating, or a transmission that jerks, slips, or fails to shift correctly. These problems don’t just make the car hard to drive—they potentially put everyone on the road at risk. If engine or transmission failures persist after several repair attempts, the vehicle may meet the legal criteria required for a lemon law claim. According to Consumer Reports, most state laws require that the defect “substantially impairs” the vehicle’s use, value, or safety, and that repairs are attempted within a set timeframe or mileage window.
Brake System Failures
The braking system is one of the most critical safety components in any vehicle, as it directly determines the driver’s ability to stop quickly and maintain control. Common defects include leaking brake fluid, faulty anti-lock braking systems (ABS), or brake pedals that feel spongy, unresponsive, or fail to engage correctly. These issues can dramatically increase stopping distances, reduce vehicle stability, or cause sudden and complete brake failure without warning. Due to the serious safety risks involved, most jurisdictions recognize that even one unresolved brake defect—despite repeated repair attempts—may qualify the vehicle for lemon law protection, thereby safeguarding consumers from dangerous manufacturing flaws.
Steering and Suspension Problems
Steering and suspension problems significantly compromise a vehicle’s safety by making it harder to control and increasing the likelihood of serious accidents. Failures such as power steering loss, sudden steering wheel lockups, or faulty suspension parts—including worn ball joints, broken struts, or damaged control arms—can lead to unstable handling and unexpected vehicle movement. These dangers are especially pronounced during high-speed driving, emergency maneuvers, or sharp turns, where precise control is critical. Because such defects directly affect drivability and occupant safety, they are typically covered under lemon laws, requiring owners to act quickly to document issues and pursue appropriate remedies.
Electrical System Malfunctions
Modern vehicles are increasingly driven by complex electrical systems that impact almost every function, from starting the engine to security and infotainment features. Some of the most problematic electrical defects are faulty vehicle sensors, dashboards that fail to display critical warnings, or persistent battery drains. Electrical defects that interfere with primary vehicle operations (for example, affecting airbag deployment or ABS brakes) may provide a strong basis for a lemon law claim. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) maintains a public database of recalls and known electrical defects affecting vehicles nationwide.
Airbag and Seatbelt Defects
Airbags and seatbelts are designed to save lives in the event of an accident. When these features do not work as intended—such as airbags failing to deploy, deploying without cause, or the seatbelts not latching correctly—the consequences can be devastating. Cars with ongoing airbag or seatbelt problems that remain unresolved after a reasonable number of repair attempts almost always fall under lemon laws, as these issues compromise fundamental safety protections.
Infotainment and Electronic Issues
Although infotainment and entertainment systems might appear secondary, their role in driver attention and overall vehicle safety is significant. Failures in these systems—such as unresponsive backup cameras, navigation interruptions, or malfunctioning screens and speakers—can divert focus and create hazardous situations. When such defects repeatedly interfere with usability or compromise safe operation, and repairs fail to resolve the issues after reasonable attempts, they may qualify as legitimate grounds for a lemon law claim. Recognizing the safety implications of these seemingly minor systems underscores the importance of addressing every defect promptly and thoroughly.
Fuel System and Emission Failures
Fuel system failures, including leaks or malfunctioning emission control systems, pose serious safety hazards and legal challenges for vehicle owners. A leaking fuel system significantly raises the risk of fire or explosion, endangering both occupants and bystanders. At the same time, faulty emissions components can render a vehicle noncompliant with state and federal environmental regulations, making it illegal to drive. These issues often lead to failed safety or emissions inspections, potential fines, and difficulties with vehicle registration. Many of these problems fall under lemon law protections, giving consumers legal recourse to address persistent fuel or emission-related defects.
Conclusion
Understanding which auto defects are commonly covered by lemon laws enables consumers to quickly identify when they may have a right to legal recourse. If your vehicle exhibits persistent and unresolved problems—whether it’s with the engine, brakes, electrical systems, or other critical safety features—contact a qualified professional to discuss your options. Knowledge of your rights and lemon law protections can help you make informed decisions and advocate effectively for your safety and financial interests.
-

 TOPIC6 months ago
TOPIC6 months agoSymbols of Hope: The 15th Belenismo sa Tarlac
-

 TOPIC6 months ago
TOPIC6 months ago“The Journey Beyond Fashion” – Ditta Sandico
-

 NEWS6 months ago
NEWS6 months agoHistorical Churches in Manila
-

 TOPIC6 months ago
TOPIC6 months agoRIZAL at 160: a Filipino Feat in Britain
-

 TOPIC6 months ago
TOPIC6 months ago5 Must-Have Products From Adarna House to Nurture Your Roots
-

 TOPIC6 months ago
TOPIC6 months agoBoats with Two Strings
-

 TOPIC6 months ago
TOPIC6 months ago“Recuerdos de Filipinas – Felix Laureano”
-

 TOPIC1 month ago
TOPIC1 month agoUnveiling AvTub: Your Ultimate Guide to the Best AV Content
